
Combined official K3s and Kubernetes logo by Zaw Zaw
This article focuses on how to setup and bootstrap the multi-node K3s cluster and how to configure automated upgrading of the K3s Kubernetes cluster. This covers both how to setup a multi-node K3s Kubernetes cluster and how to upgrade K3s automatically using the system upgrade controller.
Usually, we manually download the K3s binary file from the GitHub release page, install and upgrade it in K3s Server and Agent Kubernetes nodes. Instead, we can manage and configure automated cluster upgrading for K3s using Rancher’s system upgrade controller and Plan CRD, Custom Resource Definition.
Objectives
- Setup a Multi-node K3s Kubernetes cluster.
- Explore the System Upgrade Controller and how it works.
- Install the System Upgrade Controller on Kubernetes.
- Configure
PlanCRD to automate K3s cluster upgrade. - Monitor K3s System Upgrade
Planconfiguration and job status.
Setup K3s Kubernetes Cluster
Firstly, we need to setup and bootstrap the K3s cluster with the installation script. It’s simple to set up a Server and an Agent. In this article, I will use AWS EC2 instances to setup the K3s cluster.
We have two AWS EC2 instances:
- k3s-dev-master (K3s Server)
- k3s-dev-worker (K3s Agent)
Official K3s Documentation: https://docs.k3s.io
K3s Server (ControlPlane/Master Node)
On the k3s-dev-master instance, run the following installation script to bootstrap the K3s server, also known as Kubernetes ControlPlane/Master Node.
1
2
3
$ curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -s - server \
--write-kubeconfig-mode 644 \
--node-taint "CriticalAddonsOnly=true:NoExecute"
If you want to make your K3s server as a ControlPlane/Master only, Make sure you add CriticalAddonsOnly=true:NoExecute Node taint when bootstrapping the K3s server.
Or, alternatively, you can also add Node taints with the kubectl command-line tool.
1
2
3
$ kubectl taint node k3s-dev-master CriticalAddonsOnly=true:NoExecute
$ kubectl taint node k3s-dev-master node-role.kubernetes.io/master=true:NoSchedule
$ kubectl taint node k3s-dev-master node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane=true:NoSchedule
K3s Agent (Worker Node)
On the k3s-dev-worker instance, run the following installation script to bootstrap K3s Agent also known as Kubernetes Worker Node to join the ControlPlane/Master Node.
1
2
3
$ curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -s - agent \
--server https://<172.16.x.x>:6443 \
--token K10d47c3a1abbbc24647fc37f9531ee6d9145d485408dc19f0bf4964c82beeaf175::server:91d5e063491d81783cab2bf1e728e4f1
Explanation:
--server- Set your K3s Server’s URL that includes IP address and port number.
--token- Set your K3s Server’s token. You can find that token in your K3s Server’s file path
/var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-tokenor/var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/token.
- Set your K3s Server’s token. You can find that token in your K3s Server’s file path
To get K3s Server’s token, go to the K3s Server, k3s-dev-master instance and get the node token by running the cat command tool. The node token filepath is /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-token (or) /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/token.
For example,
1
2
$ cat /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-token
K10d47c3a1abbbc24647fc37f9531ee6d9145d485408dc19f0bf4964c82beeaf175::server:91d5e063491d81783cab2bf1e728e4f1
Add label to mark Kubernetes Worker Node as Worker role.
1
kubectl label node k3s-dev-worker node-role.kubernetes.io/worker=true
Finally, we can get nodes with kubectl command line tool
1
2
3
4
5
$ kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
k3s-dev-master Ready control-plane,master 8d v1.28.6+k3s2 172.x.x.x <none> Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS 5.15.0-94-generic containerd://1.7.11-k3s2
k3s-dev-worker Ready worker 8d v1.28.6+k3s2 172.x.x.x <none> Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS 5.15.0-94-generic containerd://1.7.11-k3s2
System Upgrade Controller
Basically, System Upgrade Controller aims to provide a general-purpose, Kubernetes-native upgrade controller for Nodes. It introduces a new Custom Resource Definition Plan for defining all of your upgrade requirements and a controller that schedules upgrades based on the configured plans.
GitHub Repository: https://github.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller
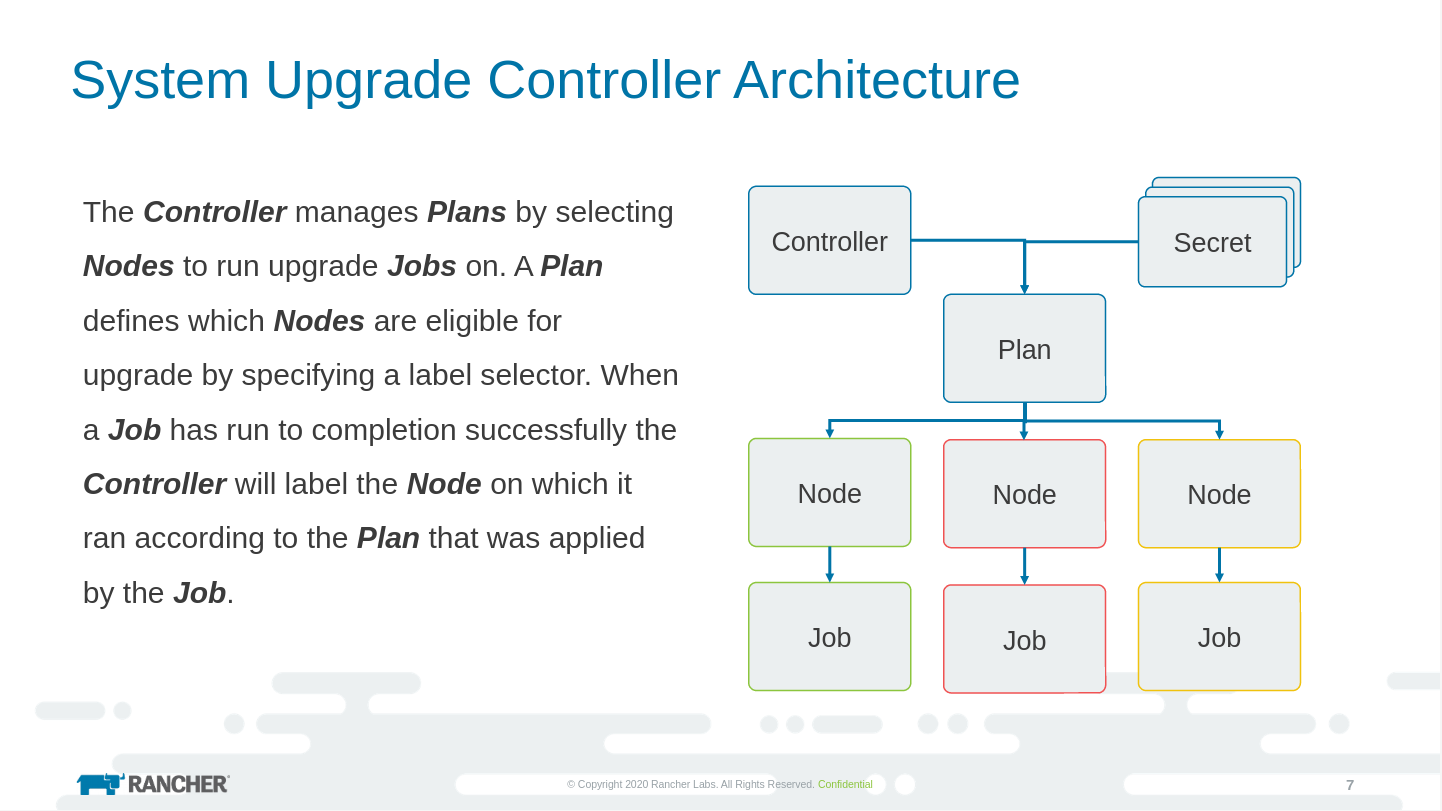 System Upgrade Controller Architecture Photo by Rancher
System Upgrade Controller Architecture Photo by Rancher
Before we configure Plan CRD for automated upgrades for K3s Kubernetes cluster, make sure you install system-upgrade-controller on your cluster.
To install the system-upgrade-controller with kubectl,
1
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller/releases/latest/download/system-upgrade-controller.yaml
This installs system-upgrade-controller Deployment and required ServiceAccount, ClusterRoleBinding and ConfigMap into system-upgrade namespace.
Configure K3s System Upgrade Plans
For configuring automated K3s cluster upgrades, make sure you configure and deploy Plan configuration on your K3s Kubernetes Cluster. Plan basically defines how we plan for your next K3s upgrades. For example; K3s version, channel, cordon, concurrency and so on.
Create a Kubernetes API resource YAML file using Plan CRD named plan-k3s-upgrade.yaml like the following example configuration. YAML filename can be as you like.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
apiVersion: upgrade.cattle.io/v1
kind: Plan
metadata:
name: plan-k3s-server-upgrade
namespace: system-upgrade
spec:
concurrency: 1
cordon: true
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/controlplane
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/etcd
operator: Exists
nodeSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
operator: In
values:
- "true"
serviceAccountName: system-upgrade
upgrade:
image: rancher/k3s-upgrade
# channel: https://update.k3s.io/v1-release/channels/stable
version: v1.28.6+k3s2
---
apiVersion: upgrade.cattle.io/v1
kind: Plan
metadata:
name: plan-k3s-agent-upgrade
namespace: system-upgrade
spec:
concurrency: 1
cordon: true
nodeSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/worker
operator: In
values:
- "true"
serviceAccountName: system-upgrade
upgrade:
image: rancher/k3s-upgrade
# channel: https://update.k3s.io/v1-release/channels/stable
version: v1.28.6+k3s2
There are important things to understand configuring the K3s Plans
spec.concurrency- Set concurrency if you want to run System Upgrade jobs concurrently.
spec.cordon- Set cordon to true if you want to enable cordon also known as mark Node as unschedulable.
spec.tolerations- Set tolerations if your ControlPlane/Master Node has taints because Plan job needs to run in Master or K3s server node. Please, see https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/taint-and-toleration
spec.nodeSelector- Set nodeSelector with key/value Node labels. Make sure you set node selector correctly to run Plan jobs on both ControlPlane/Master and Worker nodes.
spec.serviceAccountName- Set serviceAccountName. Defaults to system-upgrade service account.
spec.upgrade.image- Set K3s upgrade image. Defaults to
rancher/k3s-upgradeContainer image.
- Set K3s upgrade image. Defaults to
spec.channel- Set K3s upgrade channel https://update.k3s.io/v1-release/channels/stable.
spec.version- Set specific K3s version to upgrade. For example, current latest stable version is v1.28.6+k3s2.
We can also set spec.channel to stable or latest to upgrade automatically K3s to current latest version based on you specified K3s upgrade channel.
Default K3s upgrade channel is stable.
For example; Stable Channel
1
2
3
4
5
6
apiVersion: upgrade.cattle.io/v1
kind: Plan
...
spec
...
channel: https://update.k3s.io/v1-release/channels/stable
For example; Latest Channel
1
2
3
4
5
6
apiVersion: upgrade.cattle.io/v1
kind: Plan
...
spec
...
channel: https://update.k3s.io/v1-release/channels/latest
Please, also note that System Upgrade Job automatically upgrades to current latest K3s version when available new version in stable or latest channel if you have not specified K3s version to upgrade. It depends on you specified channel.
After configure Plans for both K3s Server and Agent, deploy the Plan resources with kubectl.
Make sure you deploy system-upgrade-controller and Plan in same system-upgrade namesapce.
1
$ kubect apply -f k3s-system-upgrade.yaml
Then, the controller will pick them up and begin to upgrade K3s to latest version based on K3s upgrade channel stable or latest if you have specified channel or specific K3s version in Plan resource.
Checking K3s System Upgrade Jobs
Finally, we can check and monitor the progress of an upgrade by viewing Plan and Jobs with kubectl command line tool.
1
2
$ kubectl get plans --namespace system-upgrade -o yaml
$ kubectl get jobs --namespace system-upgrade